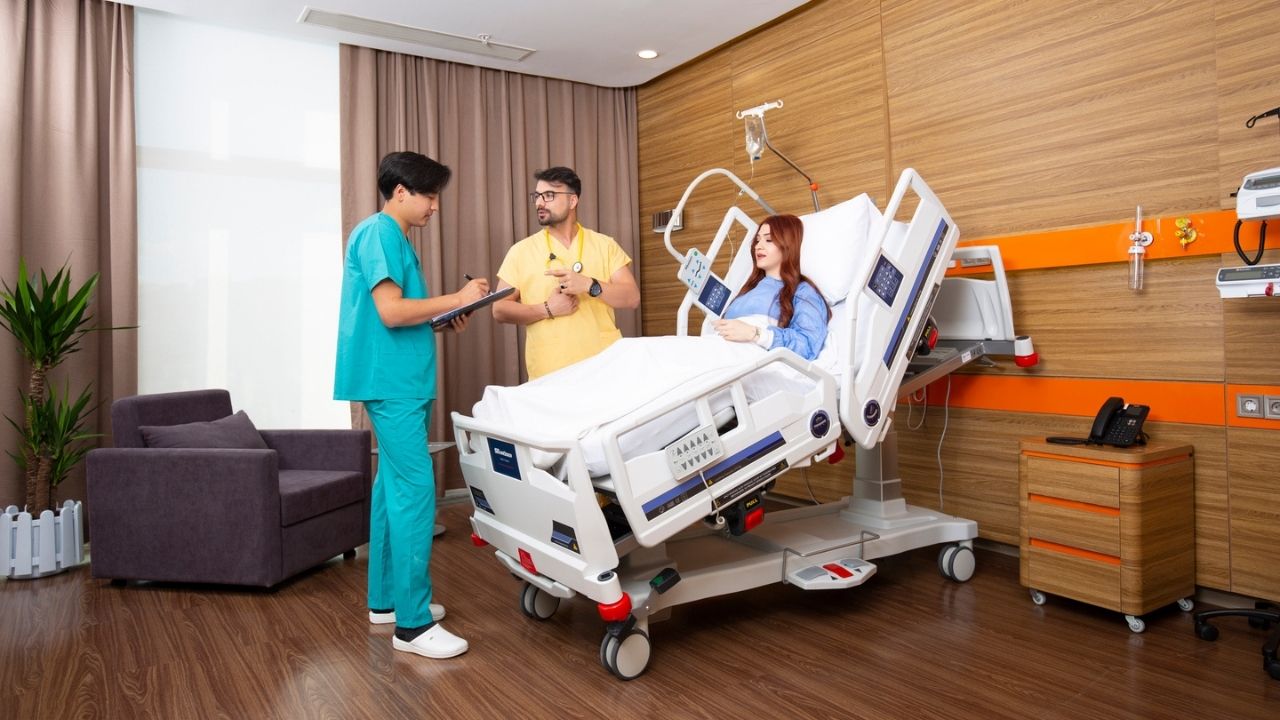
Types of hospital beds vary greatly depending on their design, purpose, and patient needs. Types of hospital beds are crucial in both hospitals and home care settings, offering comfort, safety, and functionality. There are several types of hospital beds, including manual, electric, and specialty models tailored to specific medical situations. Understanding the types of hospital beds helps healthcare providers and families choose the most suitable option. Different types of hospital beds can improve recovery by providing the right support and mobility features. This guide will explore how many types of hospital beds are there and explain their unique uses to help you make the right decision.

What Are the Main Types of Hospital Beds?
-
Manual Hospital Beds
Manual hospital beds are one of the most commonly used options in many healthcare settings. Manual hospital beds require physical effort to adjust their height and bed positions using a hand crank system. These beds are cost-effective and simple, making them ideal for facilities with limited budgets or where patient repositioning is minimal.
A major advantage of manual hospital beds is their durability and ease of maintenance. Since they do not rely on electrical components, they are less prone to technical malfunctions. However, manual beds may not be suitable for all patients, especially those who require frequent position adjustments or who have limited caregiver support. In such cases, the effort needed to manually operate the bed can be a challenge. Despite this, manual hospital beds remain a reliable and budget-friendly solution in both hospitals and home care environments.
-
Semi-Electric Hospital Beds
Semi-electric hospital beds combine the advantages of manual and fully electric systems. These beds use electric motors to adjust the head and foot sections, while the height is controlled manually with a crank. Semi-electric hospital beds offer more convenience compared to manual beds and are generally more affordable than fully electric models.
One of the key benefits of semi-electric hospital beds is their ability to improve patient comfort without fully depending on caregivers for every adjustment. The electric controls allow patients to change their head and foot positions independently, which can reduce bed sores and enhance breathing. However, since height adjustment still requires manual effort, these beds may not be ideal for all medical settings. Overall, semi-electric hospital beds offer a balanced solution for patients who need some level of independence without the higher cost of fully electric beds.
-
Fully Electric Hospital Beds
Fully electric hospital beds provide the highest level of comfort and flexibility for both patients and caregivers. These beds allow all adjustments—head, foot, and height—to be controlled with an electric handset, minimizing physical strain for both the patient and healthcare providers.
The biggest advantage of fully electric hospital beds is their ease of use and ability to be quickly adjusted to meet patient needs. These beds are especially beneficial for patients with limited mobility or those who require frequent repositioning to prevent pressure ulcers. Although fully electric hospital beds tend to be more expensive, their convenience and patient-centered features make them a popular choice in modern hospitals and home care environments. Additionally, many fully electric models come with extra safety features like side rails and battery backup systems to ensure continuous operation even during power outages.
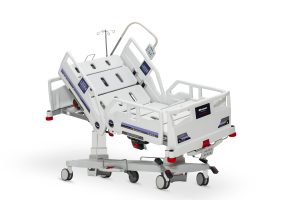
What Are the Types of Specialty Hospital Beds?
Types of specialty hospital beds are specifically designed to meet unique medical conditions and complex patient needs. These beds offer specialized features beyond standard hospital beds, providing tailored support and improving both patient safety and recovery outcomes. Types of specialty hospital beds include bariatric beds, low hospital beds, pediatric beds, and ICU beds, each serving a different clinical purpose. Understanding these specialized options is essential when selecting the most appropriate solution for critical care, obesity management, or pediatric treatment.
Bariatric Hospital Beds
Bariatric hospital beds are specifically engineered for patients who are overweight or obese. These beds have a wider frame and a higher weight capacity, typically supporting weights up to 500 kilograms. Bariatric beds provide enhanced stability and comfort, reducing the risk of bed frame failure or patient injury. One of the key features of bariatric hospital beds is their reinforced structure, which ensures safety during patient repositioning and transfer. Additionally, these beds often include heavy-duty side rails and powerful motors to handle increased loads.
Choosing bariatric beds is essential in cases where standard beds are not sufficient to meet the patient’s needs. The extra width and strength significantly contribute to patient comfort and safety. For healthcare providers, bariatric hospital beds simplify the process of moving and caring for larger patients, minimizing strain on caregivers and enhancing overall treatment efficiency.

Low Hospital Beds
Low hospital beds are designed with a reduced height to prevent falls and injuries, especially for patients at high risk of falling out of bed. These beds can be lowered very close to the floor, which reduces the impact if a patient accidentally rolls off. Low hospital beds are commonly used in nursing homes, rehabilitation centers, and home care settings where patient mobility is extremely limited.
One of the key advantages of low hospital beds is their ability to provide a safer environment for elderly patients or those with neurological conditions. Many models come with the option to raise the bed when caregivers need to perform medical procedures, offering both safety and convenience. By reducing the distance between the bed surface and the floor, these beds play a crucial role in fall prevention strategies in healthcare facilities.

Pediatric Hospital Beds
Pediatric hospital beds are specially designed for infants and children, offering a safe, size-appropriate environment. These beds often feature high, protective side rails or enclosed crib-like structures to prevent accidental falls. Pediatric hospital beds can be manual or electric, with adjustable sections to accommodate different medical treatments.
One of the main benefits of pediatric hospital beds is that they cater specifically to the size, weight, and mobility of younger patients. Some pediatric beds also include interactive elements, like bright colors or engaging designs, to create a less intimidating hospital experience for children. These specialized beds are essential in pediatric wards and help ensure that young patients receive the safest and most comfortable care possible.
CCU Hospital Beds
CCU hospital bed is a specialized type of bed designed specifically for patients in Coronary Care Units who require intensive cardiac monitoring and life-saving interventions. A CCU hospital bed typically features advanced electric adjustability, cardiac chair positioning, side rail controls, and integrated monitoring equipment to support critical care needs. These beds are engineered for maximum patient safety, allowing quick access during emergencies and precise positioning to reduce cardiac stress. The structure and functionality of a CCU hospital bed help medical staff perform procedures efficiently while keeping the patient stable and comfortable. For patients recovering from heart attacks, arrhythmias, or undergoing post-operative cardiac care, the use of a CCU hospital bed significantly enhances treatment outcomes and overall care quality.
ICU Hospital Beds
ICU hospital beds are highly advanced beds designed for intensive care units, where critically ill patients require constant monitoring and frequent repositioning. These beds typically offer full electric operation, integrated weighing systems, and advanced positioning options such as Trendelenburg and reverse Trendelenburg positions.
The primary benefit of ICU hospital beds is their ability to support life-saving interventions while maximizing patient safety. Features like cardiac chair positioning, lateral rotation, and synchronized adjustments allow healthcare teams to respond quickly to medical emergencies. These beds often include side rails with built-in control panels and additional safety mechanisms. For critical care patients, ICU hospital beds are essential for facilitating complex treatments, improving access for medical staff, and enhancing patient outcomes.
Which Hospital Bed Should You Choose Based on Patient Needs?
Types of beds in the hospital should always be selected based on individual patient conditions, mobility levels, and overall care requirements. Choosing the right bed is critical to ensure both patient safety and comfort, whether the bed is used in a hospital or home care setting. Since there are many different types of beds in hospital environments, the selection process should carefully consider the physical, emotional, and clinical needs of the patient. In this section, we will explore the essential factors that influence this decision and how you can find the perfect fit for your situation.
Selecting among the different types of hospital beds is not only about budget or features—it is about matching the bed’s capabilities to the patient’s daily needs. Patients with limited mobility may require a fully electric bed, while someone who is recovering from minor surgery might be comfortable with a manual bed. Additionally, types of hospital beds and their uses must align with the patient’s weight, movement ability, and whether the bed will be used at home or in a clinical setting. Proper selection ensures that patients remain safe, caregivers can work efficiently, and the healing process is supported effectively.
Factors to Consider: Mobility, Weight, Condition, and Usage Environment
Types of hospital beds should be evaluated based not only on the patient’s physical condition but also on where and how the bed will be used. For patients who can independently adjust their position or get in and out of bed, a semi-electric hospital bed might be sufficient and suitable for home care environments. However, for patients with severe mobility restrictions—such as those recovering from major surgeries, neurological disorders, or spinal injuries—fully electric hospital beds are usually the best choice. These beds allow effortless adjustments at the push of a button, offering both the patient and caregivers greater flexibility and convenience.
Another critical factor is the patient’s weight. 4 types of hospital beds and their specifications vary widely in terms of weight capacity. For bariatric patients, a standard bed may not offer enough support, making bariatric hospital beds essential. These beds provide added width and reinforced construction, ensuring comfort and safety. Additionally, if the patient is at high risk of pressure ulcers, types of air mattresses for hospital beds should be considered. These mattresses distribute weight more evenly and improve skin health, making them ideal for long-term care settings.
The patient’s medical condition and treatment plan also influence bed selection. For instance, patients who require constant monitoring, frequent repositioning, or advanced functionalities such as Trendelenburg positioning will benefit most from ICU hospital beds, which are designed for high-acuity care. In contrast, low hospital beds are more appropriate for patients who are stable but at risk of falls, often used in long-term care facilities or home environments with limited mobility support.
Ultimately, choosing the right bed type involves assessing mobility, weight, medical condition, and also the intended usage environment—whether it’s a hospital, rehabilitation center, or home. By considering all these aspects together, caregivers and healthcare providers can ensure the best possible outcome for the patient.
Matching the Right Bed Type to Home or Clinical Use
Types of beds in the hospital can serve both clinical and home care purposes, but not every hospital bed is appropriate for home use. In clinical settings like hospitals or rehabilitation centers, beds often come with more advanced features and may take up significant space. These different types of beds in hospital environments are designed to accommodate medical equipment and staff movement efficiently.
When considering a hospital bed for home care, the available space and the need for ease of transportation become crucial. Some types of hospital beds are bulkier, making them less practical in smaller rooms. In contrast, portable manual or semi-electric beds can be ideal for home use as they are easier to move and set up. Moreover, what are the different types of hospital beds suitable for homes depends heavily on how much caregiver assistance is available. Fully electric beds might be the best option for home care if caregivers need to frequently adjust the bed without straining themselves.
Another essential consideration is the long-term versus short-term nature of bed use. For short recovery periods, manual beds may be sufficient, while chronic conditions or terminal care typically require more specialized and adjustable beds. Whether at home or in the hospital, it is important to remember that types of specialty hospital beds are often required for unique patient needs such as pediatric care, bariatric support, or intensive care. By carefully matching the types of beds in the hospital to the environment and patient profile, both safety and quality of life can be significantly improved.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Hospital Bed Improves Care Quality
How many types of hospital beds are there? The answer reveals a wide range of options, each tailored to different patient needs and care environments. From manual hospital beds to types of specialty hospital beds, the selection is vast and highly dependent on patient mobility, weight, and the intended setting, whether in a clinical facility or at home. Understanding the 4 types of hospital beds—manual, semi-electric, fully electric, and air mattress-supported beds—is essential to ensure proper patient support and recovery. Additionally, considering types of air mattresses for hospital beds is crucial for those at high risk of developing bedsores.
Knowing what are the different types of hospital beds allows families and healthcare providers to make more informed decisions. Whether you are looking into different types of hospital beds for post-operative recovery, chronic illness management, or intensive care, the bed you choose directly impacts the patient’s comfort and safety. Specialty options like bariatric, low, pediatric, and ICU beds offer tailored solutions for more complex needs, emphasizing how critical it is to match bed features to patient conditions. Exploring different types of beds in hospital settings helps clarify which models provide the most value for specific clinical or home care scenarios. Whether you are evaluating the 5 types of hospital beds commonly used in healthcare or exploring specialty options, making the right choice enhances both patient outcomes and caregiver efficiency.
For a comprehensive selection of hospital bed models that cover all these categories, you can visit Schröder’s hospital bed collection to explore high-quality, safe, and durable options that meet modern care standards.



