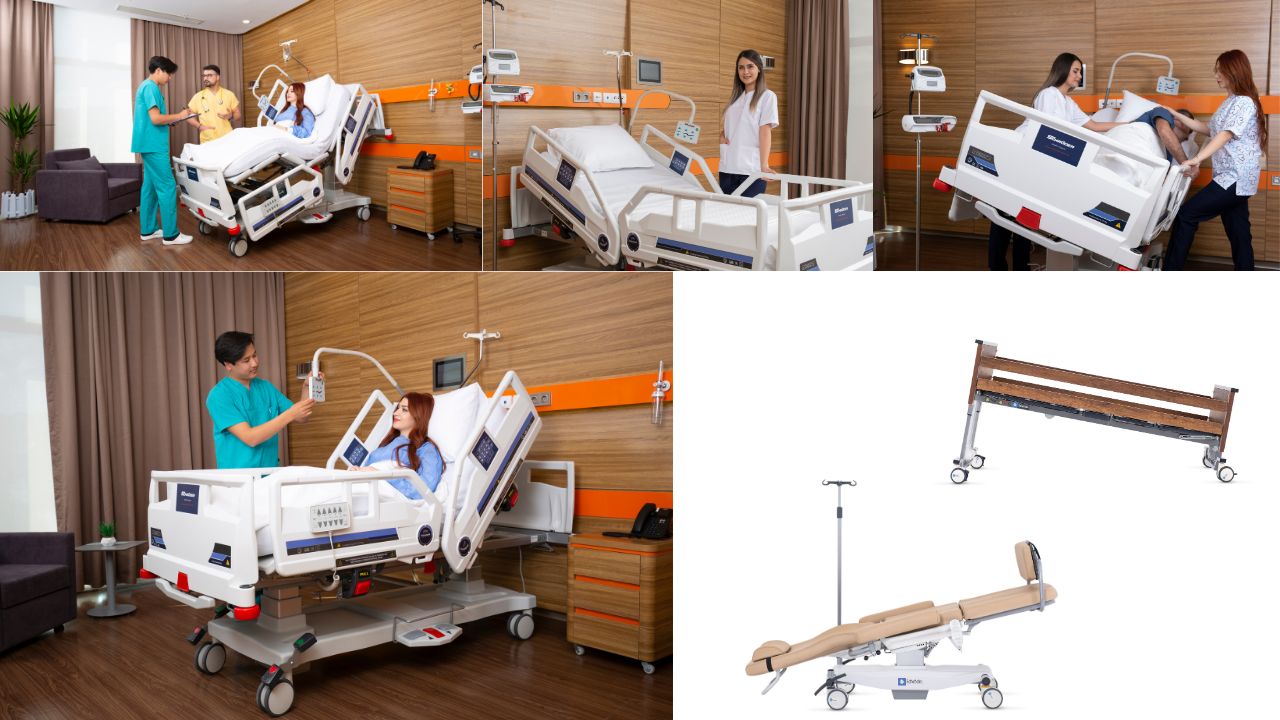
Bed positions for patients are an essential part of hospital care, ensuring both comfort and safety for individuals who are recovering or undergoing treatment. Patient positioning is the practice of placing a patient in the hospital bed in a way that supports medical needs, prevents complications, and improves well-being. The right patient bed positions can help enhance breathing, promote circulation, reduce pain, and support the healing process. In addition, medical bed positions make it easier for healthcare professionals to carry out procedures effectively. Whether for post-surgical recovery, long-term care, or diagnostic purposes, proper positions for patients in bed are a cornerstone of high-quality healthcare. This guide provides a detailed overview of common bed positions, best practices, and health benefits to help caregivers achieve optimal positioning in bed for patients.
Why Bed Positioning Matters
Patient bed positions are not just about keeping someone comfortable—they are an important medical practice that can determine the speed and quality of recovery. For example, specific hospital bed positions can prevent pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, by relieving pressure points. Adjusting the position of the patient can improve breathing for individuals with respiratory problems and help manage pain after surgery. Additionally, positioning of the patient in bed allows healthcare providers to perform essential tasks such as dressing wounds, administering treatments, or conducting physical therapy without unnecessary strain for either the patient or the caregiver.
The importance of medical positions in bed extends beyond basic comfort. For patients with heart disease, elevating the upper body can reduce strain on the heart, while those with neurological conditions may require very specific bed patient positioning to avoid injury. Using correct positions in hospital bed can also help prevent aspiration pneumonia in patients who have difficulty swallowing. Hospitals rely on proper bed positioning for patients with diagrams as training tools to ensure staff follow the safest and most effective methods. In short, bed patient position is a vital component of medical care that directly impacts health outcomes and quality of life.
Common Bed Positions Used in Hospitals
Fowler’s
Fowler’s position involves seating the patient in a semi-upright posture with the bed’s head raised between 45° and 60°. This bed position medical is ideal for patients with breathing difficulties, cardiac conditions, or those eating in bed. It reduces pressure on the diaphragm and promotes lung expansion. Variations include low, semi, and high Fowler’s.
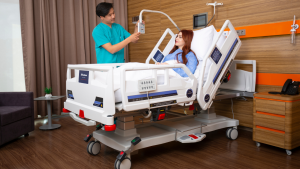
Lateral
The lateral position places the patient on their side, supported by pillows. This positioning of the patient in bed reduces pressure on the back and promotes better blood flow. It is also helpful for patients with certain spinal injuries and is used in many nursing procedures to prevent bedsores.
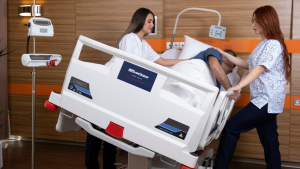
Trendelenburg
Trendelenburg position tilts the patient so their head is lower than their feet. This positions in bed medical approach is often used during surgery or for patients with low blood pressure. It can help improve circulation to vital organs, but must be used cautiously, especially for patients with head injuries or breathing problems.

Reverse Trendelenburg
In the reverse Trendelenburg position, the patient is tilted with the head higher than the feet. This position of the patient in bed is often used to improve respiratory function, reduce pressure on the head, and assist in certain surgical procedures. It can also help prevent aspiration in patients with swallowing difficulties.

Semi Fowler
Semi Fowler position places the patient in a reclined posture with the head of the bed elevated at approximately 30° to 45°. This bed patient positioning is commonly used for patients who require moderate elevation to improve breathing without placing too much pressure on the lower back. It is also ideal for post-abdominal surgery recovery, as it reduces strain on the incision site while promoting lung expansion.

Cardiac Chair
The cardiac chair position allows patients to be placed in an upright, seated posture using a hospital bed’s adjustment functions. This positions for patients in bed configuration is particularly beneficial for patients with heart or lung conditions, as it promotes optimal lung expansion and reduces the workload on the heart. It is also useful for long-term bedridden patients to prevent deconditioning.

Vascular
The vascular position involves elevating the patient’s legs above heart level to promote venous return and reduce swelling in the lower extremities. This bed position in hospital is frequently used after vascular surgeries or in patients with circulatory issues. It helps reduce edema, improve blood flow, and minimize the risk of deep vein thrombosis.
Supine
The supine position involves lying flat on the back with the head and shoulders slightly elevated. This is one of the most common positions for patients and is often used for rest, recovery, and examinations. It supports spinal alignment and allows easy access for procedures such as catheter insertion or wound care. However, long-term use without repositioning may increase the risk of pressure injuries.

“This bed position demonstrates the ideal posture for the supine position.”
Prone
In the prone position, the patient lies on their stomach with the head turned to one side. This position bed patients is particularly beneficial for improving oxygenation in patients with severe respiratory distress, such as those with ARDS. It helps expand the lungs and improves oxygen exchange. However, this position requires careful monitoring to avoid neck strain or skin breakdown.

“This bed position demonstrates the ideal posture for the prone position.”
Positioning Techniques and Best Practices
Bed position hospital care requires both knowledge and skill. Caregivers should assess the patient’s needs, mobility level, and medical condition before choosing a patient position on bed. Supporting devices such as pillows, wedges, and adjustable beds can be used to maintain the desired positioning of patients in bed safely. Frequent repositioning—typically every two hours—helps prevent complications like bedsores and joint stiffness.
In addition, bed position in hospital care should include proper body mechanics for the caregiver to avoid injury. This means bending at the knees, keeping the back straight, and using assistive devices when necessary. Following these bed patient positioning techniques ensures patient comfort, reduces risk, and supports medical recovery goals.
How Does Bed Positioning Affect Patient Health?
Correct positioning in bed for patients has significant health benefits. It can improve respiratory function, enhance circulation, and reduce swelling in certain conditions. Poor position of the patient in bed can lead to muscle atrophy, reduced lung capacity, or even life-threatening complications.
How Schröder Health Hospital Beds Support Proper Patient Positioning
Schröder Health offers advanced hospital bed systems with features such as the Trendelenburg function and adjustable backrests, making it easier to achieve the ideal positions for patients without causing discomfort. As a trusted manufacturer of hospital furniture, Schröder provides solutions designed for durability, patient safety, and caregiver convenience. Their innovative designs allow smooth adjustments, ensuring each bed patient position can be achieved quickly and safely. You can explore their products, including adjustable hospital bed, for more details.
Mistakes to Avoid While Repositioning
Common errors in bed patient positioning include failing to support pressure points, moving the patient without proper body mechanics, and leaving them in one position for too long. Ignoring these factors can lead to skin breakdown, discomfort, or injury. Caregivers should also ensure that medical devices, such as catheters or IV lines, are not strained during repositioning.
Key Points on Patient Positioning
Position bed patients correctly to prevent complications, promote healing, and ensure comfort. Use appropriate positions in hospital bed based on medical needs, and adjust regularly to prevent pressure injuries. Leverage advanced equipment, like adjustable beds from Schröder Health, to achieve optimal medical bed positions efficiently. Always prioritize safety, comfort, and individual care requirements.